Enviraj Consulting
Online Tools
| Avg. Recharge Rate (m/min) | Recharge Capacity (LPH) | Verdict | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diff | Difff | Difff | Difff | Difff |
Note:
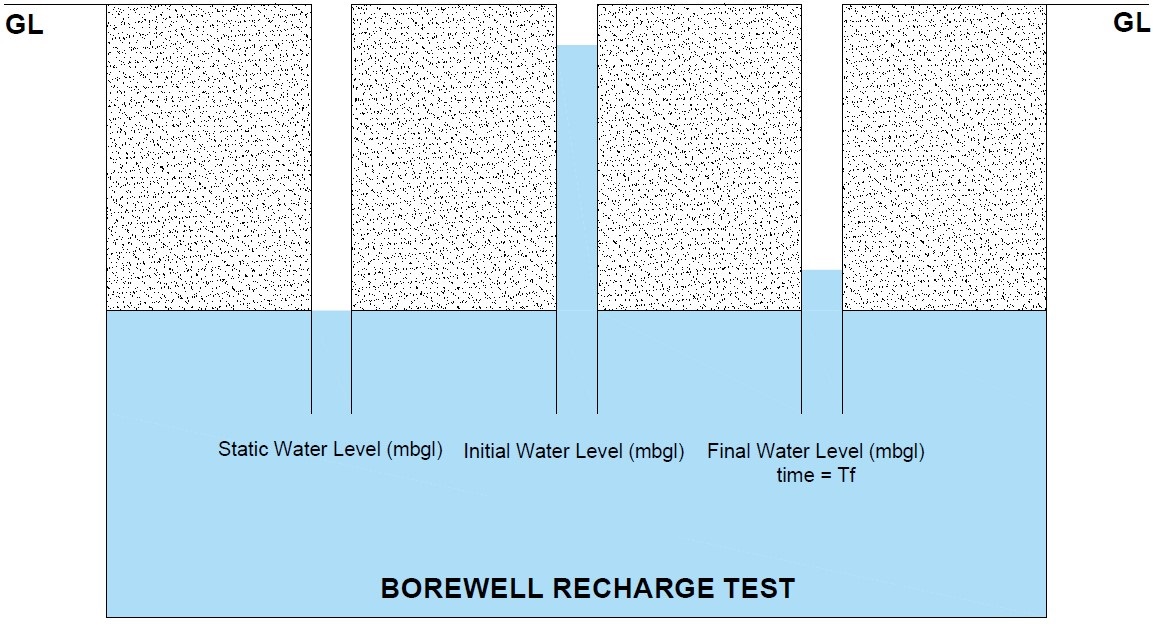
- Ideally, the final water level should return near to static water level within 30 mins. If this takes longer time, the well is considered inefficient and hence not recommended for groundwater replenishment.
- Depending upon volume of water to be recharged, number of recharge wells can be increased to enhance the recharge rate
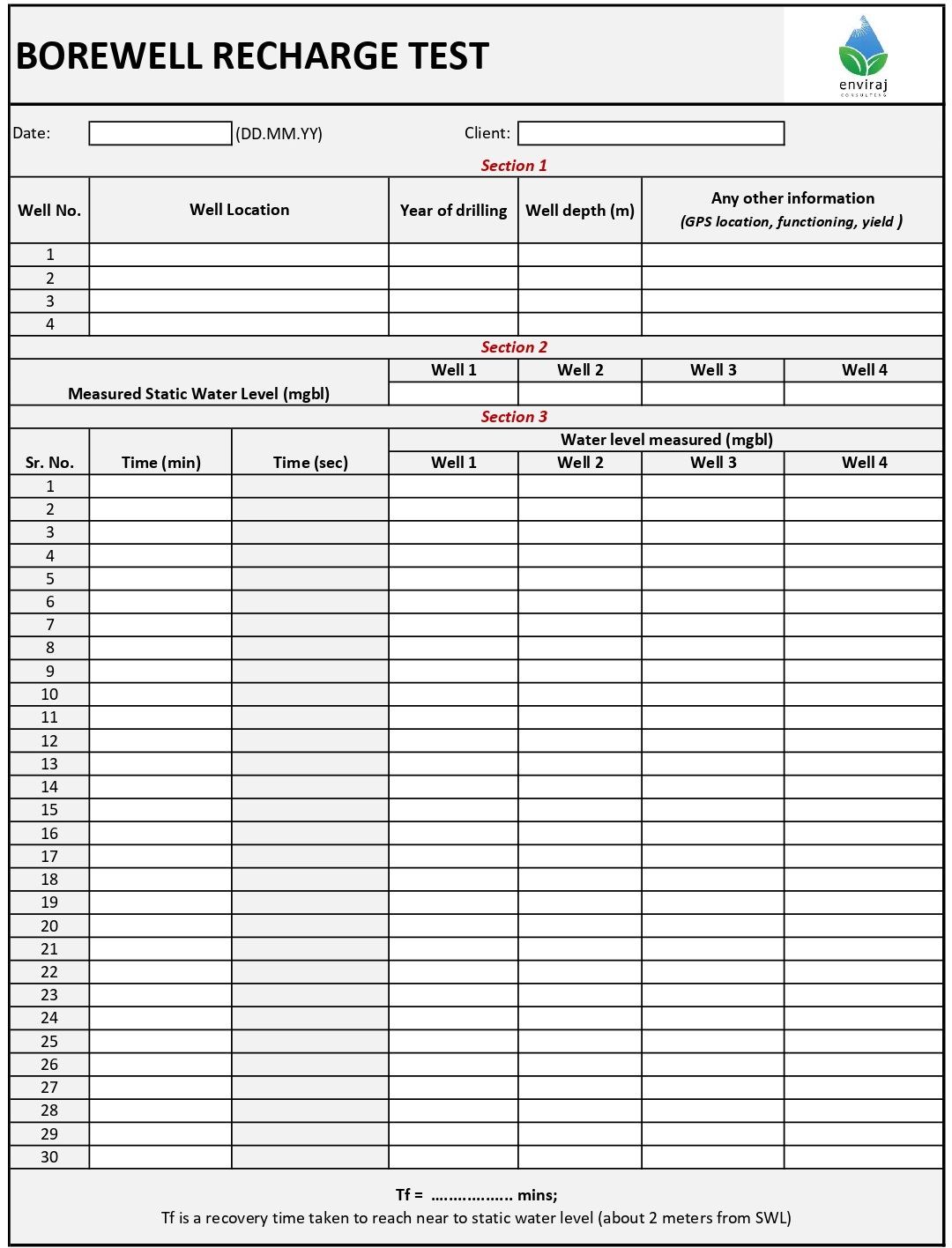
- Recharge test field sheet (Sample)
We appreciate any comments and tips on how to make our online tools a better information source. If you find any faults, inaccuracies, or otherwise unacceptable information, please contact us by email info@enviraj.com